The Schengen Rules Explained
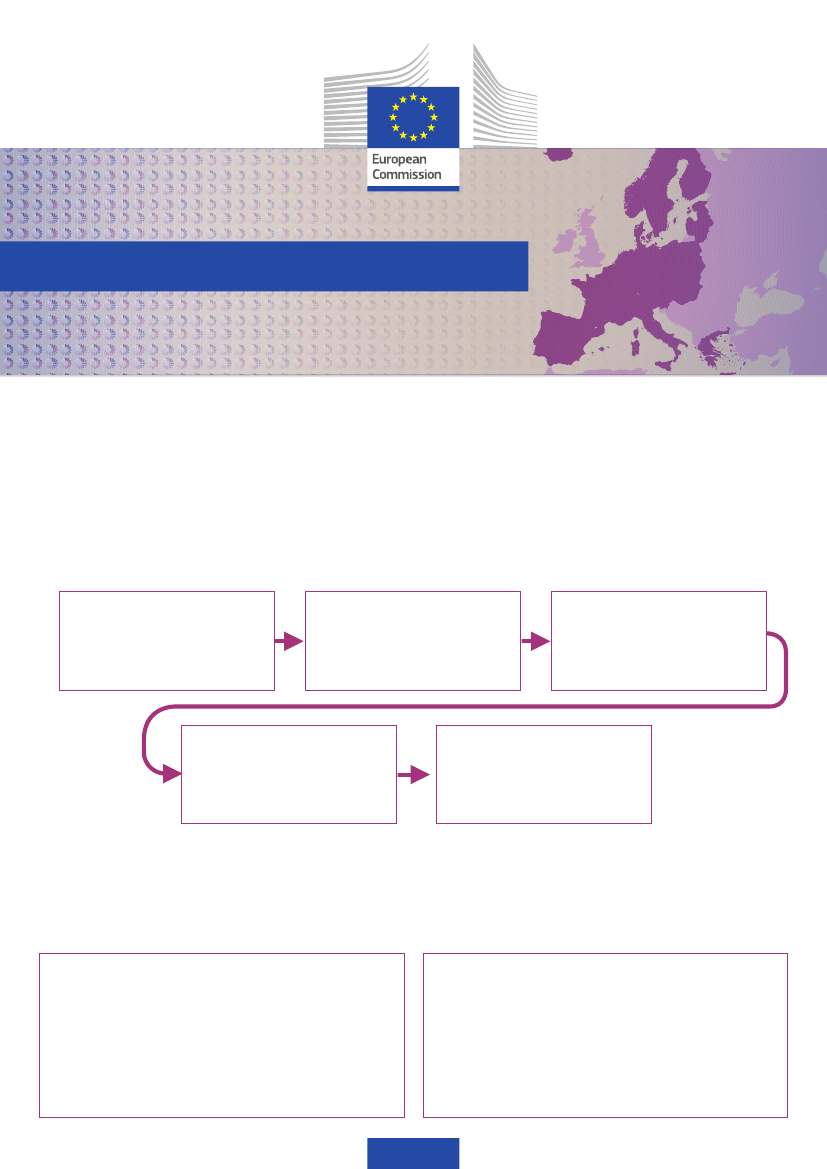
The Schengen Evaluation Mechanism
The Schengen evaluation mechanism provides for monitor-
ing visits to Member States on an annual and multi-annual
basis. On average, 5-7 Member States are evaluated each
year. The evaluation visits are carried out by Commission-
led teams with experts from Member States and Frontex.
The visits can be announced or unannounced.
Following each visit, a Schengen Evaluation Report is
drawn up and agreed by the Schengen evaluation commit-
tee of member state experts. If the report identifies any
weaknesses in management of the external border, then
recommendations for remedial action are presented. The
recommendations are submitted by the Commission to the
Council for adoption.
Commission establishes
multi-annual and annual
evaluation programmes
in cooperation with Frontex
Commission and Member States
experts conduct on-site visits
Schengen Evaluation Report iden-
tifying shortcomings adopted by
the Commission after opinion of a
Committee of the Member States
Council adopts recommendations
for remedial action upon proposal
from the Commission
Evaluated Member State submits
Action Plan to remedy weaknesses
identified
Articles 23, 24 and 25:
Temporary Reintroductions of border controls by
Member States
The Schengen Borders Code provides Member States with the possibility to temporarily reintroduce controls at internal
borders where there is a serious threat to public policy or internal security.
Article 25 – Temporary Reintroduction of Border
Controls for Unforeseen Circumstances
•
Article 25 can be used in cases requiring immediate
Article 23 and 24– Temporary Reintroduction of
Border Controls for Foreseen Circumstances
•
Article 24 can be used for foreseeable circumstances
action
•
The reintroduction is for an initial period of 10 days.
•
This can be renewed for additional periods of 20
days, up to a maximum of
2 months
in total.
if notified in advance.
•
These controls may last for an initial period of 30
days, renewable up to a maximum of
6 months.