Socialudvalget 2012-13
SOU Alm.del Bilag 333
Offentligt
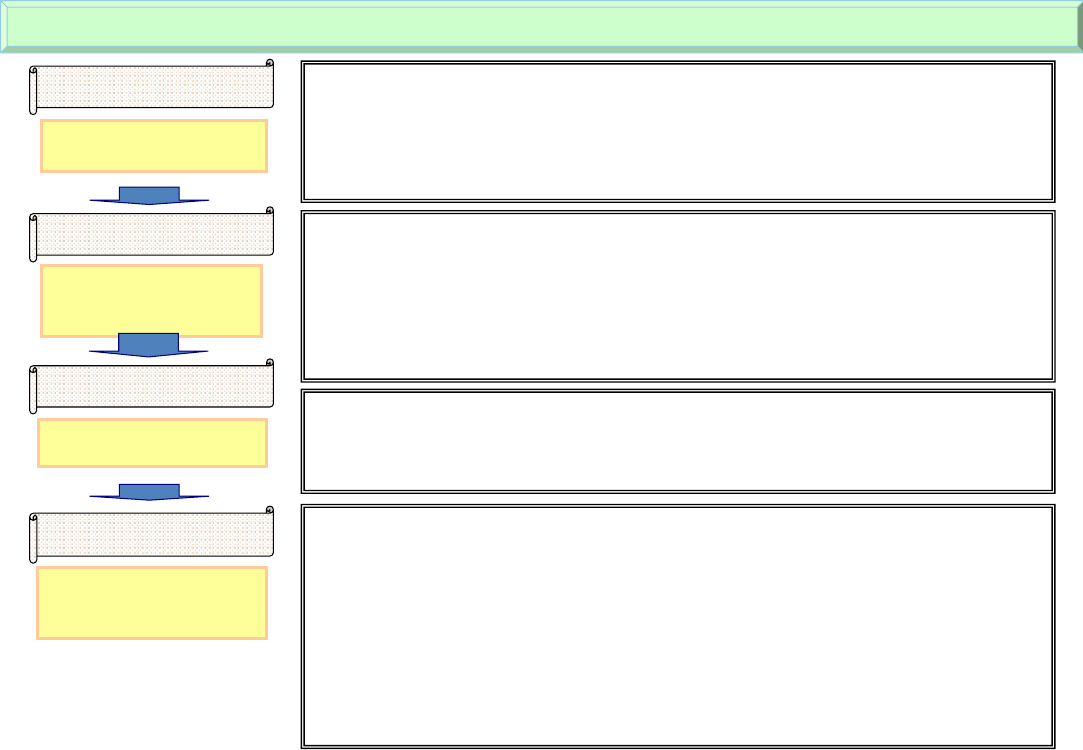
Changing social security systemThe base for the current social security system was built in the 1960s to 70s during the high-growth period after the post-war reconstruction period.Post-war disorder, urgent support for the poor
Showa 20s (1945-1954)
Post-war emergency support & infrastructure development (so-called “poor relief”)
Rapid economic growth &improvement of living standard
Showa 30s-40s (1955-1974)
Development of universal health insurance and pension systems and social security system(from so-called “poor relief” to “antipoverty”)
Global trend in social security after World War II: Growing dependence on government administration and financeWW II and the subsequent East-West conflict urged enhancement of social security as a measure against the spread of socialism.Building on key guidelines for social security reforms in place (e.g. Beveridge Report in the U.K.), reforms to aggressively enhance social securitywere conducted through the 1970s.- Basic characteristics: Poverty prevention, respect for rights to receive benefits, a comprehensive and universal social insurance system,improvement of benefits.*This brought a crucial change to trends in social security among developed countries.(1) Dependence on government finance increased due to (i) financial assistance to the insured who are unemployed and less capable ofbearing the burden and to insurers with low financial capacity and (ii) procurement of financial resources required for improving benefits.(2) The national government’s responsibility for social insurance management and finances expanded.Showa 50s-60s (1975-1988)
End of high economic growth &administrative/fiscal reform
Shift to steady growth and review of the social security system
Declining birth rate, bursting of the bubbleeconomy, & long-term economic slump
Heisei period
Structural reform of the social security system to adapt it to an aging society with fewer children
*Social security expenditure in Japan’s social security is smaller than that of other countries.
Changing social security systemShowa 20sPost-war disorder, urgentsupport for the poorPost-war emergency support and infrastructure development (so-called “poor relief”)1946 Public Assistance Act established1947 Child Welfare Act established1948 Medical Care Act, Medical Practitioners Act established1949 Act on Welfare of Physically Disabled Persons established1950 Recommendation by Advisory Council (Recommendation on the Social Security System)
Showa 30s-40sRapid economic growth &improvement of livingstandard
Development of universal health insurance and pension systems and social security system (from so-called “poor relief” to“antipoverty”)1958 National Health Insurance Act revised (universal health insurance)1959 National Pension Act established (universal pension)1961 Universal health insurance and pension systems implemented1963 Act on Social Welfare Service for Elderly established1973 First Year of Welfare (Act on Social Welfare Service for Elderly revised [free medical fees for the elderly), Health Insurance Act revised[70% benefits to family members, high-cost medical care benefit), pension system revised [increase in benefit level, benefits indexed toprices/wages])Shift to steady growth and review of the social security system1982 Health and Medical Services Act for the Aged established (introduction of partial fee payment, etc.)1984 Health Insurance Act, etc. revised (90% benefits to the insured, retiree medical care system)1985 Pension system revised (introduction of the basic pension, optimization of benefit level, establishment of pension rights to women);Medical Care Act revised (regional medical care plan)Structural reform of the social security system to adapt it to an aging society with fewer children1989 Gold Plan established1990 Eight welfare laws, incl. Act on Social Welfare Service for Elderly, revised (promotion of in-home welfare service, integration of welfareservices into municipal services)1994 Angel Plan & New Gold Plan establishedPension system revised (raising the pensionable age for the fixed amount portion of the employees’ pension, etc.)1997 Long-Term Care Insurance Act established1999 New Angel Plan established2000 Long-term care insurance launched2003 Act on Advancement of Measures to Support Raising Next-Generation Children and Basic Act for Measures to Cope with Society withDeclining Birthrate established2004 Pension system reform (introduction of macroeconomic slide mechanism for inter-generational fairness, etc.)2005 Long-term care insurance reform (conversion to prevention-centered systems, creation of community-based services)2006 Medical care system reform (comprehensive promotion of optimization of medical care costs, etc.)
Showa 50s-60sEnd of high economic growth &administrative/fiscal reform
Heisei periodDeclining birth rate, bursting ofthe bubble economy, & long-term economic slump