Europaudvalget 2011-12
EUU Alm.del Bilag 145
Offentligt
FVM 962
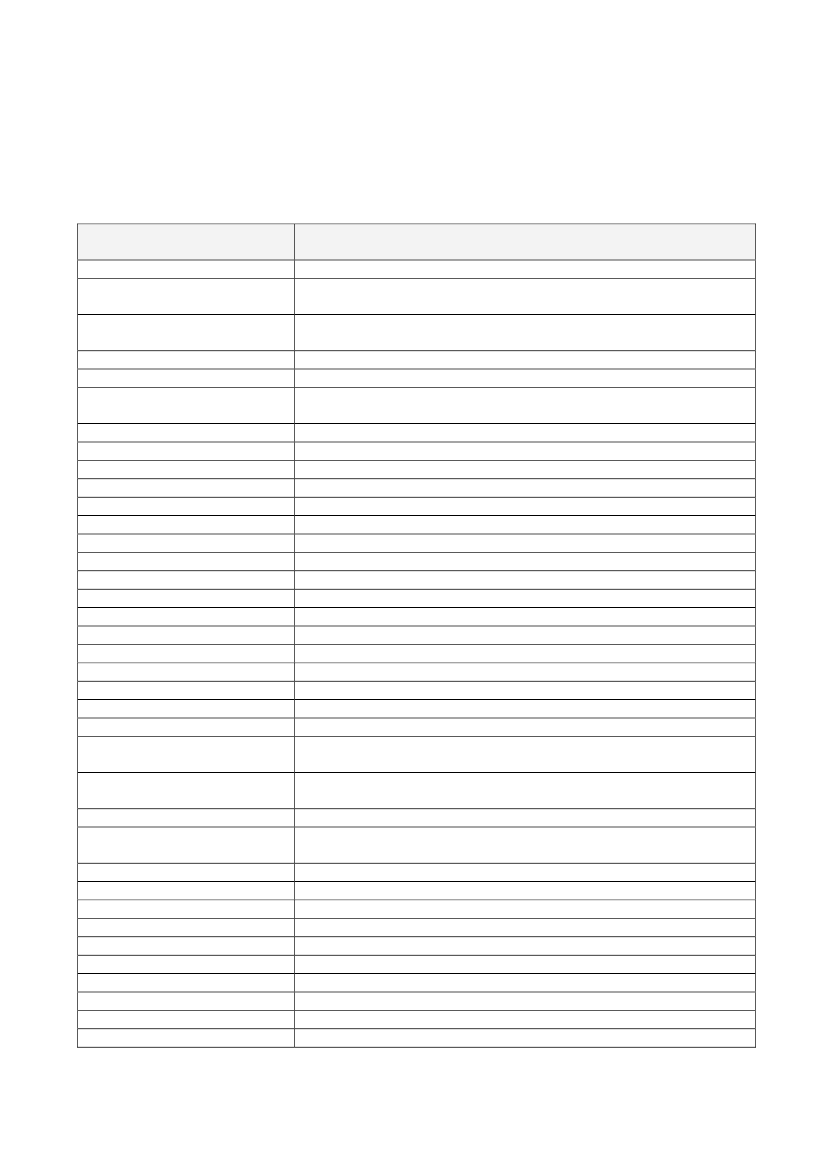
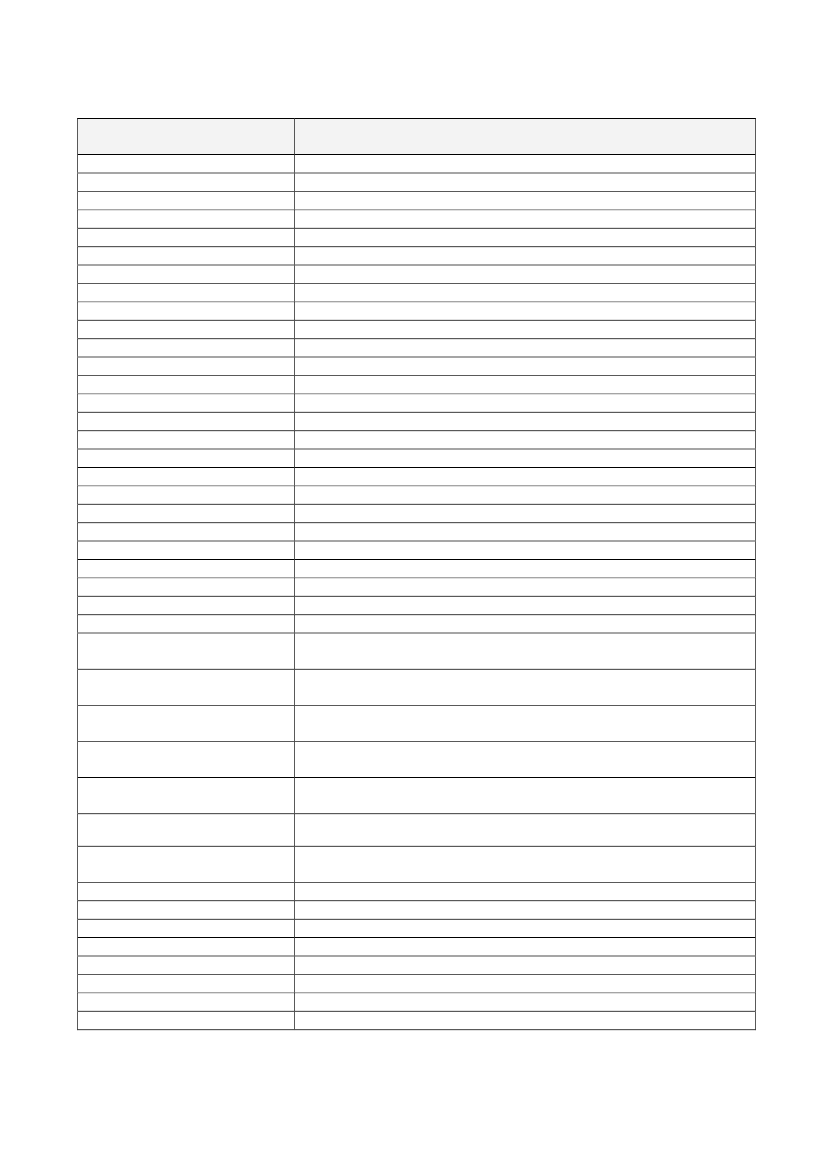
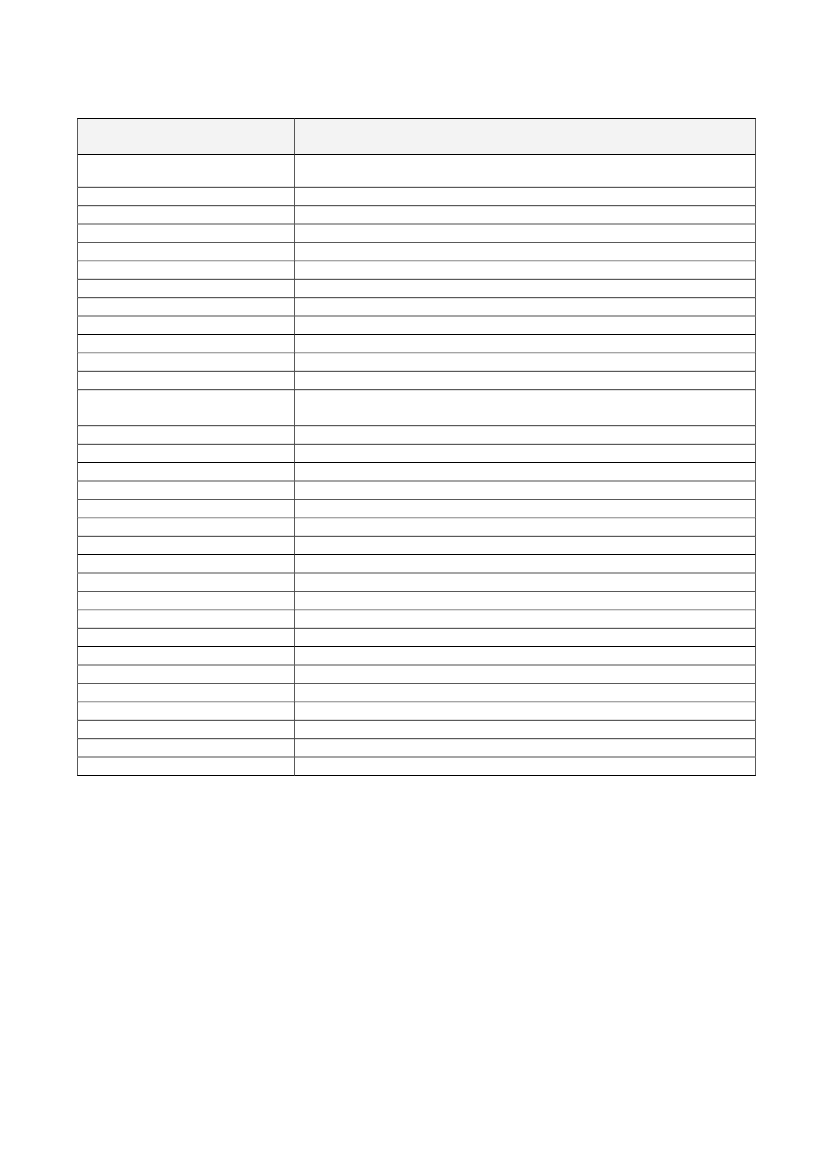
AnnexList of permitted health claimsNutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryActivated charcoalAlpha-linolenic acid (ALA)Arabinoxylan produced from wheatendospermBarley grain fibreBeta-glucansBeta-glucans from oats and barleyBetaineBiotinBiotinBiotinBiotinBiotinBiotinBiotinCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCalciumCarbohydrate-electrolyte solutionsCarbohydrate-electrolyte solutionsChitosanChlorideCholineCholineCholineChromiumChromiumCopperCopperCopperCopperCopperClaimActivated charcoal contributes to reducing excessive flatulence after eatingAlpha-linolenic acid contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterollevelsConsumption of arabinoxylan as part of a meal contributes to a reduction of theblood glucose rise after that mealBarley grain fibre contributes to an increase in faecal bulkBeta-glucans contribute to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levelsConsumption of beta-glucans from oats or barley as part of a meal contributes tothe reduction of the blood glucose rise after that mealBetaine contributes to normal homocysteine metabolismBiotin contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismBiotin contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemBiotin contributes to normal macronutrient metabolismBiotin contributes to normal psychological functionBiotin contributes to the maintenance of normal hairBiotin contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranesBiotin contributes to the maintenance of normal skinCalcium contributes to normal blood clottingCalcium contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismCalcium contributes to normal muscle functionCalcium contributes to normal muscle function and neurotransmissionCalcium contributes to normal neurotransmissionCalcium contributes to the normal function of digestive enzymesCalcium has a role in the process of cell division and differentiation.Calcium is needed for the maintenance of normal bonesCalcium is needed for the maintenance of normal teethCarbohydrate-electrolyte solutions contribute to the maintenance of enduranceperformance during prolonged endurance exerciseCarbohydrate-electrolyte solutions enhance the absorption of water duringphysical exerciseChitosan contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levelsChloride contributes to normal digestion by production of hydrochloric acid inthe stomachCholine contributes to normal homocysteine metabolismCholine contributes to normal lipid metabolismCholine contributes to the maintenance of normal liver functionChromium contributes to normal macronutrient metabolismChromium contributes to the maintenance of normal blood glucose levelsCopper contributes to maintenance of normal connective tissuesCopper contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismCopper contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemCopper contributes to normal hair pigmentationCopper contributes to normal iron transport in the body
Copper contributes to normal skin pigmentationCopper contributes to the normal function of the immune systemCopper contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressCreatine increases physical performance in successive bursts of short-term, highCreatineintensity exerciseDocosahexanoic acid (DHA)DHA contributes to maintenance of normal brain functionDocosahexanoic acid (DHA)DHA contributes to the maintenance of normal visionEPA/DHAEPA and DHA contribute to the normal function of the heartFluorideFluoride contributes to the maintenance of tooth mineralisationFolateFolate contributes to maternal tissue growth during pregnancyFolateFolate contributes to normal amino acid synthesisFolateFolate contributes to normal blood formationFolateFolate contributes to normal homocysteine metabolismFolateFolate contributes to normal psychological functionFolateFolate contributes to the normal function of the immune systemFolateFolate contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueFolateFolate has a role in the process of cell divisionFoods with a low content ofReducing consumption of saturated fat contributes to the maintenance of normalsaturated fatty acidsblood cholesterol levelsReducing consumption of sodium contributes to the maintenance of normalFoods with a low content of sodiumblood pressureConsumption of fructose containing foods leads to a lower blood glucose riseFructosethan consumption of sucrose or glucose containing foodsGlucomannanGlucomannan contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levelsGlycaemic carbohydratesGlycaemic carbohydrates contribute to the maintenance of normal brain functionGuar GumGuar gum contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levelsHydroxypropyl methylcelluloseConsumption of Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with meals contributes to a(HPMC)reduction in the blood glucose rise after those mealsHydroxypropyl methylcelluloseHydroxypropyl methylcellulose contributes to the maintenance of normal blood(HPMC)cholesterol levelsIodineIodine contributes to normal cognitive functionIodineIodine contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismIodineIodine contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemIodineIodine contributes to the maintenance of normal skinIodine contributes to the normal production of thyroid hormones and normalIodinethyroid functionIronIron contributes to normal cognitive functionIronIron contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismIronIron contributes to normal formation of red blood cells and haemoglobinIronIron contributes to normal oxygen transport in the bodyIronIron contributes to the normal function of the immune systemIronIron contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueIronIron has a role in the process of cell divisionGlucomannan in the context of an energy restricted diet contributes to weightKonjac mannan (glucomannan)lossLactase enzyme improves lactose digestion in individuals who have difficultyLactase enzymedigesting lactoseLactuloseLactulose contributes to an acceleration of intestinal transitLinoleic acidLinoleic acid contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels
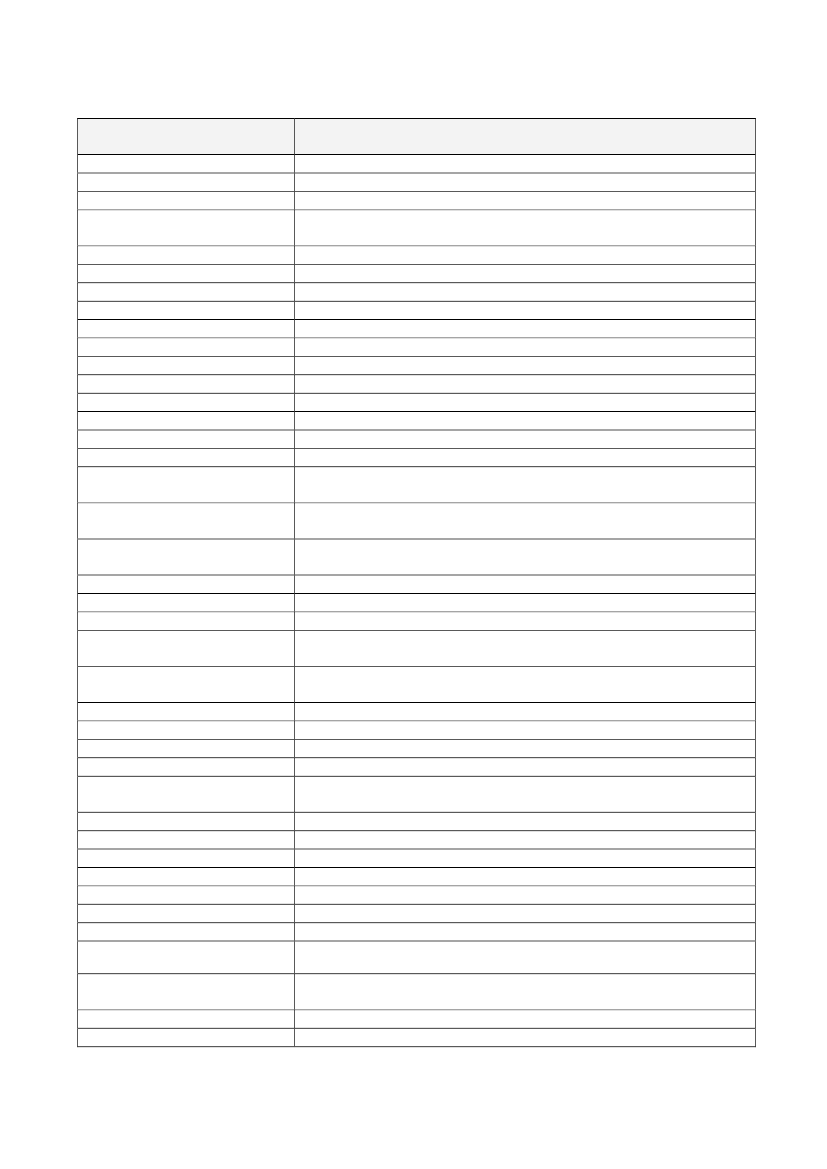
Nutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryCopperCopperCopper
Claim
Nutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryLive yoghurt cultures
Claim
Live cultures in yoghurt or fermented milk improve lactose digestion of theproduct in individuals who have difficulty digesting lactoseMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to a reduction of tiredness and fatigueMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to electrolyte balanceMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to normal muscle functionMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to normal protein synthesisMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to normal psychological functionMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesMagnesiumMagnesium contributes to the maintenance of normal teethMagnesiumMagnesium has a role in the process of cell divisionManganeseManganese contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismManganeseManganese contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesManganeseManganese contributes to the normal formation of connective tissueManganeseManganese contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressSubstituting one daily meal of an energy restricted diet with a meal replacementMeal replacement for weight controlcontributes to the maintenance of weight after weight lossSubstituting two daily meals of an energy restricted diet with meal replacementsMeal replacement for weight controlcontributes to weight lossMeat or fish contributes to the improvement of iron absorption when eaten withMeat or fishother foods containing ironMelatoninMelatonin contributes to the alleviation of subjective feelings of jet lagMelatoninMelatonin contributes to the reduction of time taken to fall asleepMolybdenumMolybdenum contributes to normal sulphur amino acid metabolismMonascus purpureous (red yeastMonacolin K from red yeast rice contributes to the maintenance of normal bloodrice)cholesterol levelsMonounsaturated and/orpolyunsaturated fatty acidsNiacinNiacinNiacinNiacinNiacinNiacinOat grain fibreOleic acidPantothenic AcidPantothenic AcidPantothenic AcidPantothenic AcidPectinsPectinsPhosphorusReplacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats in the diet contributes to themaintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels. [MUFA and PUFA areunsaturated fats]Niacin contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismNiacin contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemNiacin contributes to normal psychological functionNiacin contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranesNiacin contributes to the maintenance of normal skinNiacin contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueOat grain fibre contributes to an increase in faecal bulkReplacing saturated fats in the diet with unsaturated fats contributes to themaintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels. Oleic acid is an unsaturated fat.Pantothenic acid contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismPantothenic acid contributes to normal synthesis and metabolism of steroidhormones, vitamin D and some neurotransmittersPantothenic acid contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatiguePantothenic contributes to normal mental performancePectins contribute to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levelsConsumption of pectins with meals contributes to the reduction of the bloodglucose rise after those mealsPhosphorus contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolism
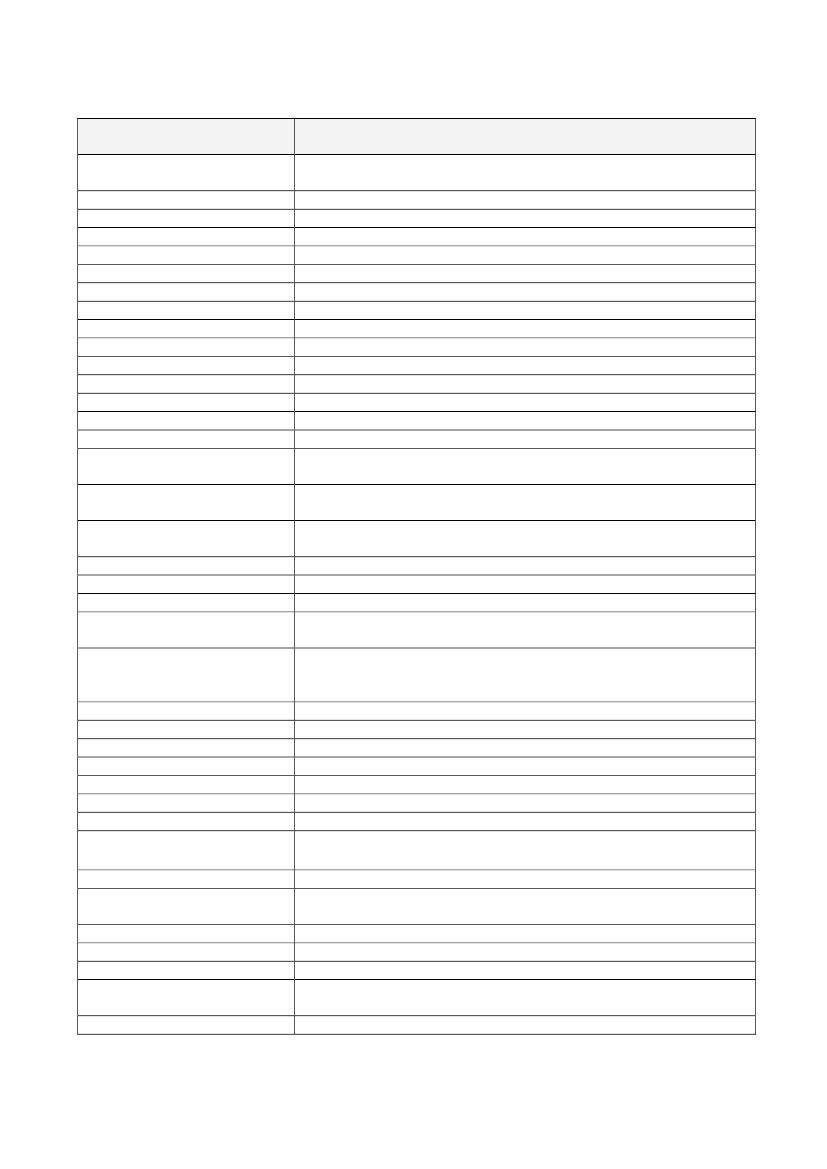
Nutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryPhosphorusPhosphorusPhosphorusPlant sterols and plant stanolsPolyphenols in olive oilPotassiumPotassiumPotassiumProteinProteinProteinResistant starchRiboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)Rye fibreSeleniumSeleniumSeleniumSeleniumSeleniumSeleniumSugar replacers, i.e. intensesweeteners; xylitol, sorbitol,mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, sucralose andpolydextrose; D-tagatose andisomaltuloseSugar replacers, i.e. intensesweeteners; xylitol, sorbitol,mannitol, maltitol, lactitol, isomalt,erythritol, sucralose andpolydextrose; D-tagatose andisomaltuloseSugar-free chewing gumSugar-free chewing gumSugar-free chewing gumSugar-free chewing gum withcarbamideThiamineThiamine
ClaimPhosphorus contributes to normal function of cell membranesPhosphorus contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesPhosphorus contributes to the maintenance of normal teethPlant sterols/stanols contribute to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterolOlive oil polyphenols contribute to the protection of blood lipids from oxidativestressPotassium contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemPotassium contributes to normal muscle functionPotassium contributes to the maintenance of normal blood pressureProtein contributes to a growth in muscle massProtein contributes to the maintenance of muscle massProtein contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesReplacing digestible starches with resistant starch at meals contributes to areduction in the blood glucose rise after those meals.Riboflavin contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismRiboflavin contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemRiboflavin contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranesRiboflavin contributes to the maintenance of normal red blood cellsRiboflavin contributes to the maintenance of normal skinRiboflavin contributes to the maintenance of normal visionRiboflavin contributes to the normal metabolism of iron in the bodyRiboflavin contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressRiboflavin contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueRye fibre contributes to normal bowel functionSelenium contributes to normal spermatogenesisSelenium contributes to the maintenance of normal hairSelenium contributes to the maintenance of normal nailsSelenium contributes to the normal function of the immune systemSelenium contributes to the normal thyroid functionSelenium contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressConsumption of foods/drinks containing <name of sugar replacer> instead ofsugar* induces a lower blood glucose rise after their consumption compared tosugar-containing foods/drinks* In the case of D-tagatose and isomaltulose thisshould read "other sugars"
Consumption of foods/drinks containing <name of sugar replacer> instead ofsugar* contributes to the maintenance of tooth mineralisation* In the case of D-tagatose and isomaltulose this should read "other sugars"Sugar-free chewing gum contributes to the maintenance of tooth mineralizationSugar-free chewing gum contributes to the neutralisation of plaque acidsSugar-free chewing gum contributes to the reduction of oral drynessSugar-free chewing gum with carbamide neutralises plaque acids moreeffectively than sugar-free chewing gums without carbamideThiamine contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismThiamine contributes to normal functioning of the nervous system
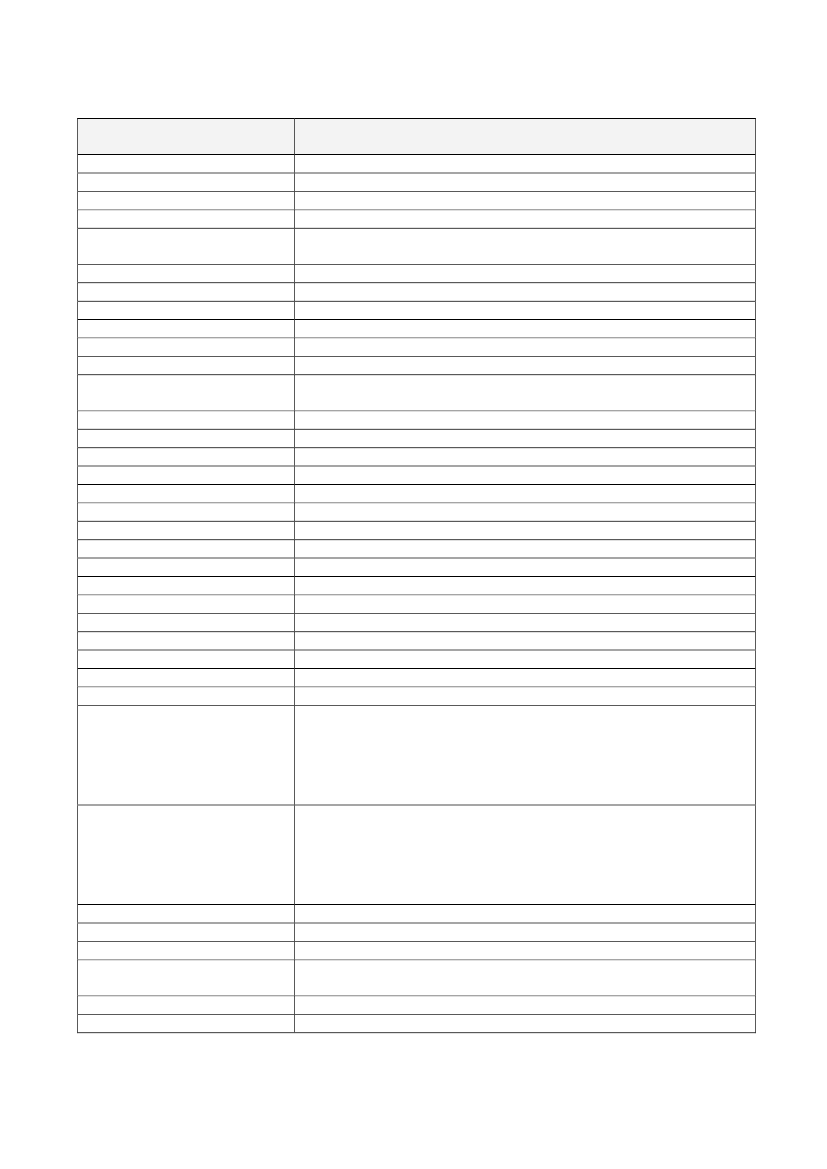
Nutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryThiamineThiamineVitamin AVitamin AVitamin AVitamin AVitamin AVitamin AVitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B12Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin B6Vitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin CVitamin C
ClaimThiamine contributes to normal psychological functionThiamine contributes to the normal function of the heartVitamin A contributes to normal iron metabolismVitamin A contributes to the maintenance of normal mucous membranesVitamin A contributes to the maintenance of normal skinVitamin A contributes to the maintenance of normal visionVitamin A contributes to the normal function of the immune systemVitamin A has a role in the process of cell specialisationVitamin B12 contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismVitamin B12 contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemVitamin B12 contributes to normal homocysteine metabolismVitamin B12 contributes to normal psychological functionVitamin B12 contributes to normal red blood cell formationVitamin B12 contributes to the normal function of the immune systemVitamin B12 contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueVitamin B12 has a role in the process of cell divisionVitamin B6 contributes to normal cysteine synthesisVitamin B6 contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismVitamin B6 contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemVitamin B6 contributes to normal homocysteine metabolismVitamin B6 contributes to normal protein and glycogen metabolismVitamin B6 contributes to normal psychological functionVitamin B6 contributes to normal red blood cell formationVitamin B6 contributes to the normal function of the immune systemVitamin B6 contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueVitamin B6 contributes to the regulation of hormonal activityVitamin C contributes to maintain the normal function of the immune systemduring and after intense physical exerciseVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofblood vesselsVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofbonesVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofcartilageVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofgumsVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofskinVitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function ofteethVitamin C contributes to normal energy-yielding metabolismVitamin C contributes to normal functioning of the nervous systemVitamin C contributes to normal psychological functionVitamin C contributes to the normal function of the immune systemVitamin C contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressVitamin C contributes to the reduction of tiredness and fatigueVitamin C contributes to the regeneration of the reduced form of vitamin EVitamin C increases iron absorption
Nutrient, substance, food or foodcategoryVitamin DVitamin DVitamin DVitamin DVitamin DVitamin DVitamin DVitamin EVitamin KVitamin KWalnutsWaterWaterWheat bran fibreWheat bran fibreZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZincZinc
ClaimVitamin D contributes to normal absorption/utilisation of calcium andphosphorusVitamin D contributes to normal blood calcium levelsVitamin D contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesVitamin D contributes to the maintenance of normal muscle functionVitamin D contributes to the maintenance of normal teethVitamin D contributes to the normal function of the immune systemVitamin D has a role in the process of cell divisionVitamin E contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressVitamin K contributes to normal blood clottingVitamin K contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesWalnuts contribute to the improvement of the elasticity of blood vesselsWater contributes to the maintenance of normal physical and cognitive functionsWater contributes to the maintenance of normal regulation of the body'stemperatureWheat bran fibre contributes to an acceleration of intestinal transitWheat bran fibre contributes to an increase in faecal bulkZinc contributes to normal acid-base metabolismZinc contributes to normal carbohydrate metabolismZinc contributes to normal cognitive functionZinc contributes to normal DNA synthesisZinc contributes to normal fertility and reproductionZinc contributes to normal macronutrient metabolismZinc contributes to normal metabolism of vitamin AZinc contributes to normal protein synthesisZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal bonesZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal hairZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal nailsZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal skinZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal testosterone levels in the bloodZinc contributes to the maintenance of normal visionZinc contributes to the normal function of the immune systemZinc contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative stressZinc has a role in the process of cell division