Udenrigsudvalget 2010-11 (1. samling)
URU Alm.del Bilag 99
Offentligt
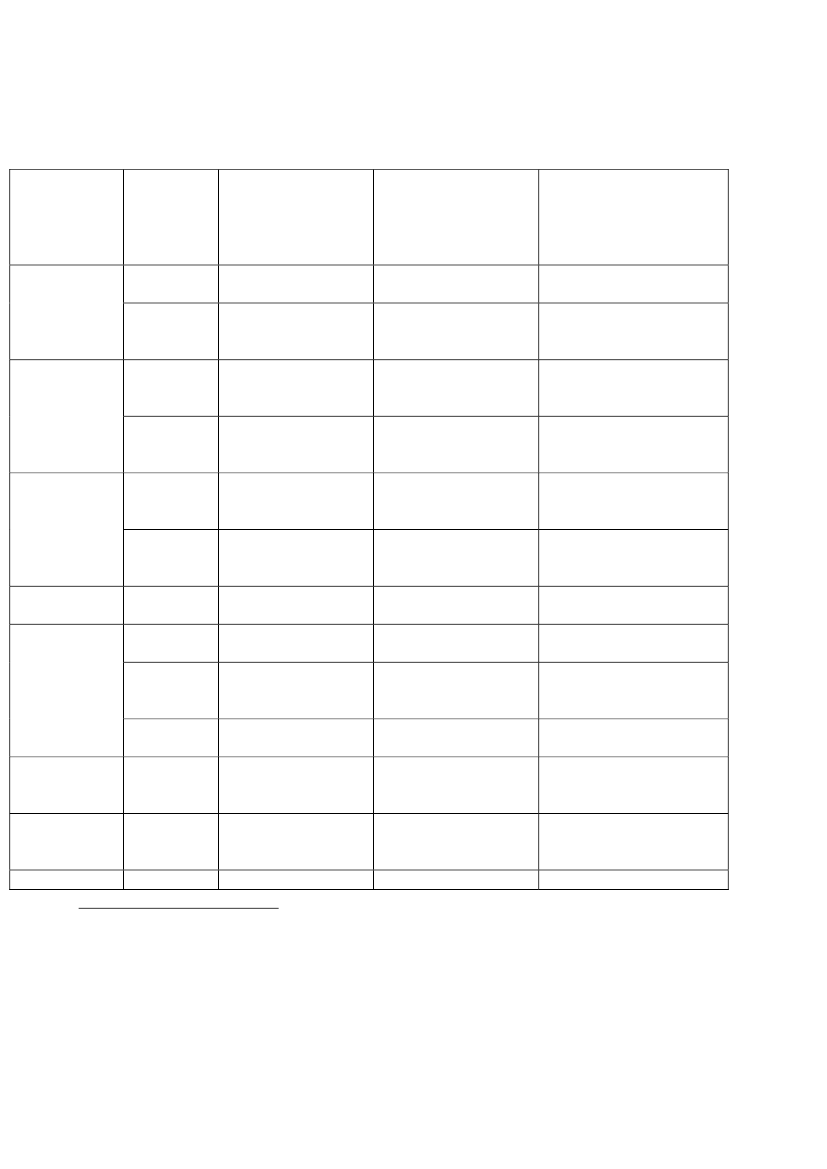
Snapshot of Significant Supplies to Egypt1Country ofSupplyCzechRepublic
Date ofDeliveryLicense2005-20092009
Category ofEquipmentRevolvers and Pistols
Trade Value ofdelivery (D) orlicensesauthorised (L)$4,219,338 (D)
Source ofInformationUN customs data –Comtrade category 89114EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML6UN customs data –Comtrade category 89129EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML11EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML11EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML6UN customs data –Comtrade category 89111UN customs data –Comtrade category 89131UN customs data –Comtrade category 89129UN customs data –Comtrade category 89122EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML6EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML6UN customs data –
Ground vehicles and€2,165,687 (L)Components€1, 530,603 (D)Munitions of War $3,002,762 (D)(bombs,grenades,etc)Electronic equipment€2,409,695 (L)Electronic equipment
France
2005-20092009
Germany
20092009
€51,924, 901 (L)
Ground vehicles and€19,836,769 (L)ComponentsTanks and Armoured $7,007,680 (D)vehiclesNon-military firearms $5,079,419 (D)
IndiaItaly
20092005-2009
2005, 2007 Munitions of War $9,731,781(D)& 2009(bombs,grenades,etc)2005-2009Shotgun cartridges$2,346,934 (D)TheNetherlandsPolandSlovakia1
200920092005-2009
Ground vehicles and€1,202,476 (L)ComponentsGround vehicles and€1,318,295 (L)ComponentsTanks and Armoured $16,900,742 (D)
This table of significant suppliers has been compiled to provide a snapshot of some arms transfers that have beenlicensed for export or already delivered to Egypt. It includes the types of equipment that have been used or couldpotentially be used to commit or facilitate serious violations of human rights by the Egyptian security forces. Reports,media footage and other material have already shown a range of equipment, including tear gas and water cannons,have been used to repress the protestors. Information on the licensing and actual delivery of arms export isnotoriously lacking in detail. Categories are often vague and seldom is there indication of the intended end-use andend-user. These are among several of the concerns raised by Amnesty International and other organisations aboutthe level of transparency and, therefore, accountability of government-published reporting on arms exports.
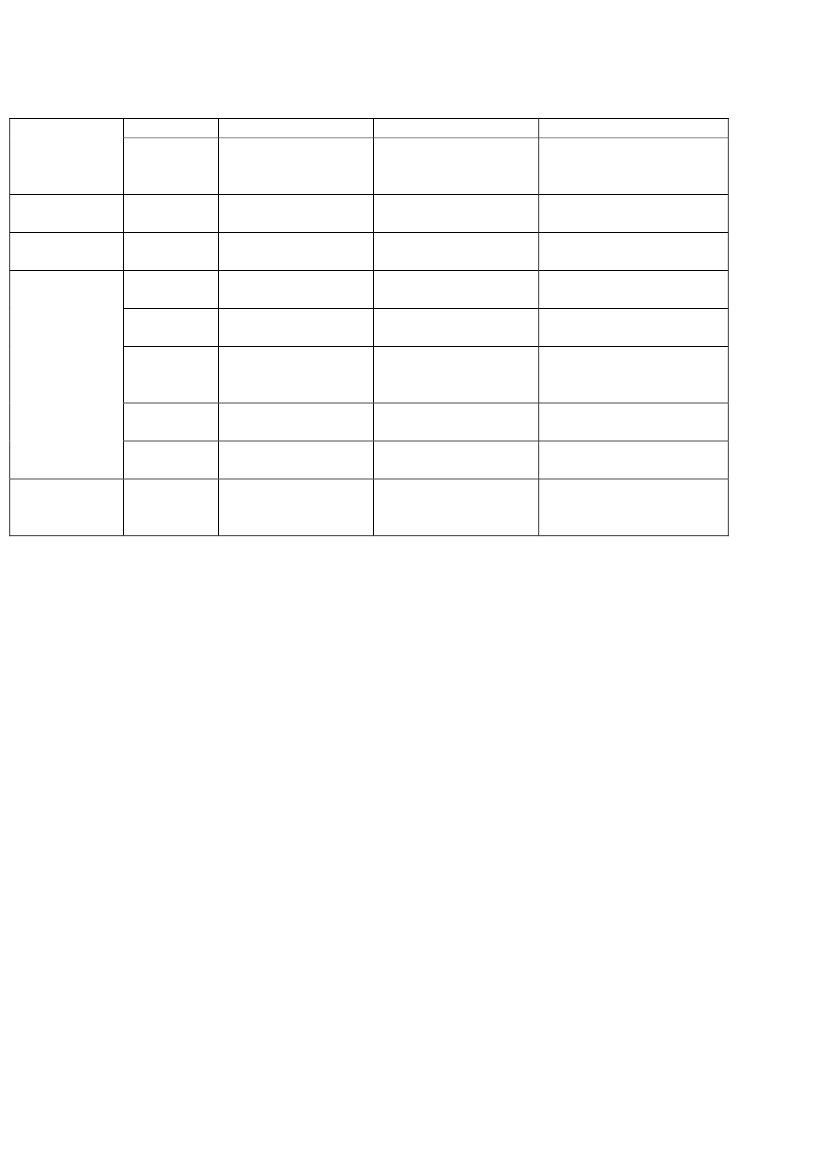
2009South KoreaSwitzerlandUSA20082005-20092005-20092005-20092005-20092005-20092005-2009UK2009
vehiclesGround vehicles and€23,682,208 (L)Components€5,530, 766 (D)Cartridges (other than $4,824,147 (D)for shotguns)Military weapons$3,722,641 (D)Tanks and ArmouredvehiclesMilitary weapons$1,002,988,633 (D)$412,156,800 (D)
Munitions of War $358,940,989 (D)(bombs,grenades,etc)Cartridges (other than $60,092,010 (D)for shotguns)Non-military firearms $24,922,114 (D)Electronic equipment
Comtrade category 89111EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML6UN customs data –Comtrade category 89124UN customs data –Comtrade category 89112UN customs data –Comtrade category 89111UN customs data –Comtrade category 89112UN customs data –Comtrade category 89129UN customs data –Comtrade category 89124UN customs data –Comtrade category 89131EU annual report on armsexports in 2009 – categoryML11
€1,681,844 (L)