Udvalget for Fødevarer, Landbrug og Fiskeri 2010-11 (1. samling)
FLF Alm.del Bilag 34
Offentligt
Environmental Risk Assessment ofHerbicide Tolerant GM plants.Jeremy Sweet(EFSA GMO Panel)
DK Conference,29 October 2010,Copenhagen1
EC GMO Regulations
•2001/18/EC:Impacts of changes incultivation, management and harvestingtechniques associated with the GMO
2
GMO Panel ERA Guidance Document
ERA include environmental impactsof the specific cultivation andmanagement of GM plants.(cfconventional plants)ERA GM herbicide tolerant (HT)crops: evaluate theenvironmental consequencesand impact of herbicideprogrammes associated withGMHT crops, (+ environmentalimpacts of GM plant itself).
Being revised in 2010
3
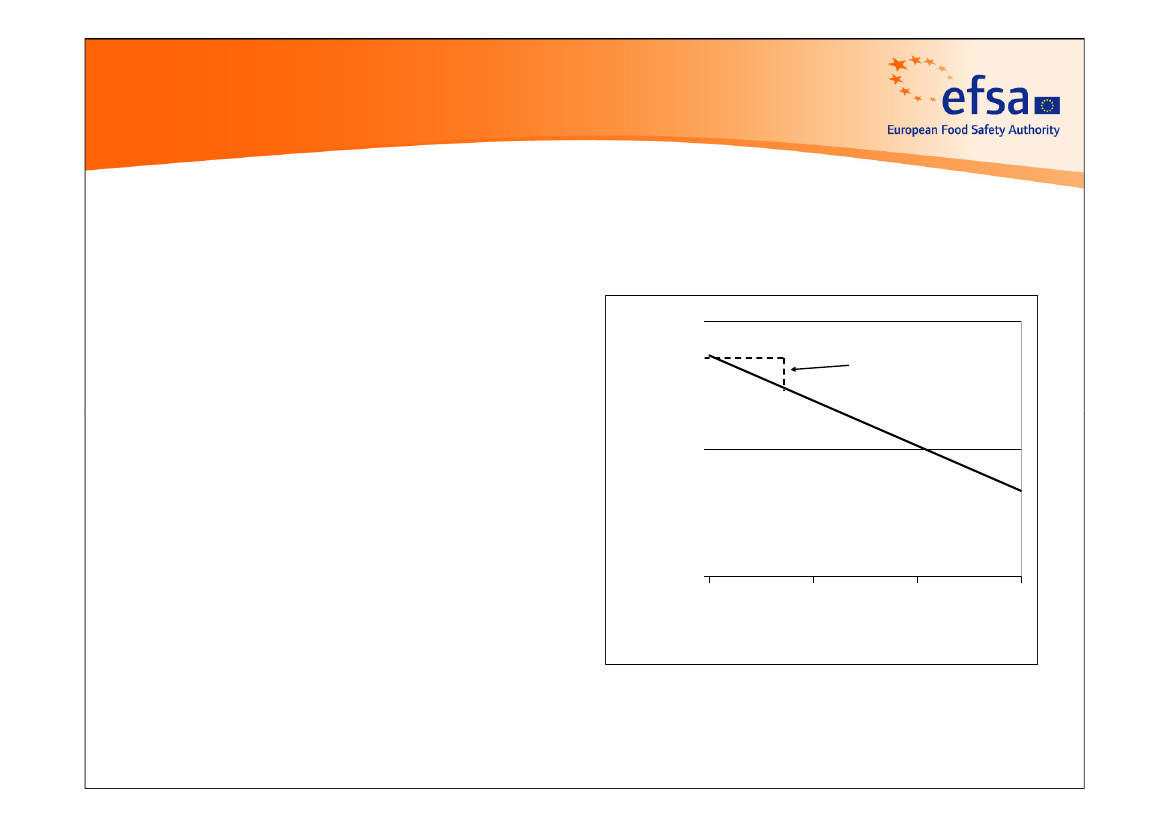
Herbicide EffectsSeed bank decline
100000
seedbank (m-2)
Abundance fallslogarithmically when allplants are prevented fromre-seedingChange was originallydetected after 2 years inearlier field experiments(1920s to 1950s)
when is thischange firstdetectable?10000
1000
0
2
4
6
period of intense fallow (year)
Brenchley & Warington 1933Roberts 1958, 19624
Herbicide Effects•Herbicides exclude most weed plants from crop andimmediately surrounding area•Crop contains little botanical diversity (species xnumber of plants)•Base of food chain removed – effects food chainreduction in diversity (sp x n) of phytophagus spp(incl. fungi, bacteria, arthropods etc..)reduction in diversity of other species: predators,parasites etc…
*Main cause of reductions in farmlandbiodiversity in Europe( inc. farmland birds)5
Environmental Effects of Herbicides:
Env effects of herbicides depend on:
•
••••••••
Active ingredient (contact, systemic,residual, broad spectrum, selective, etc.)Formulation and additives (surfactants,wetters, etc)Tank mix (other pesticides etc..)Amount applied (dose),Number of applicationsTiming (in relation to plant development)Targeting and precision < > DriftOther agronomic practices (No Till systems)6Crop rotations
Effects of GMHT ManagementConsiderable research data has shown potential forGMHT crops to change botanical and bio-diversity.
7
Environmental Risk Assessment•UK Farm Scale Evaluation of HT crops• Recognition that main Env impacts will come from theuse/management of the herbicides• Therefore ERA of GM plant + management
8
Environmental Effects of Herbicides:
Management more important than a.i.• Careful management of glyphosate > less Env harmthan excessive use of more selective H.• Allows minimum tillage• More targeted application… better precision.• Management measures* being applied to H in manyMS to reduce environmental impact..- Unsprayed margins of fields (eg 6-12 m)- Max dose & no of applications- Timing & frequency of use in crop or rotation- Drift control measures ( droplet size, windconditions) ……………..*Legal Requirements with penalties9
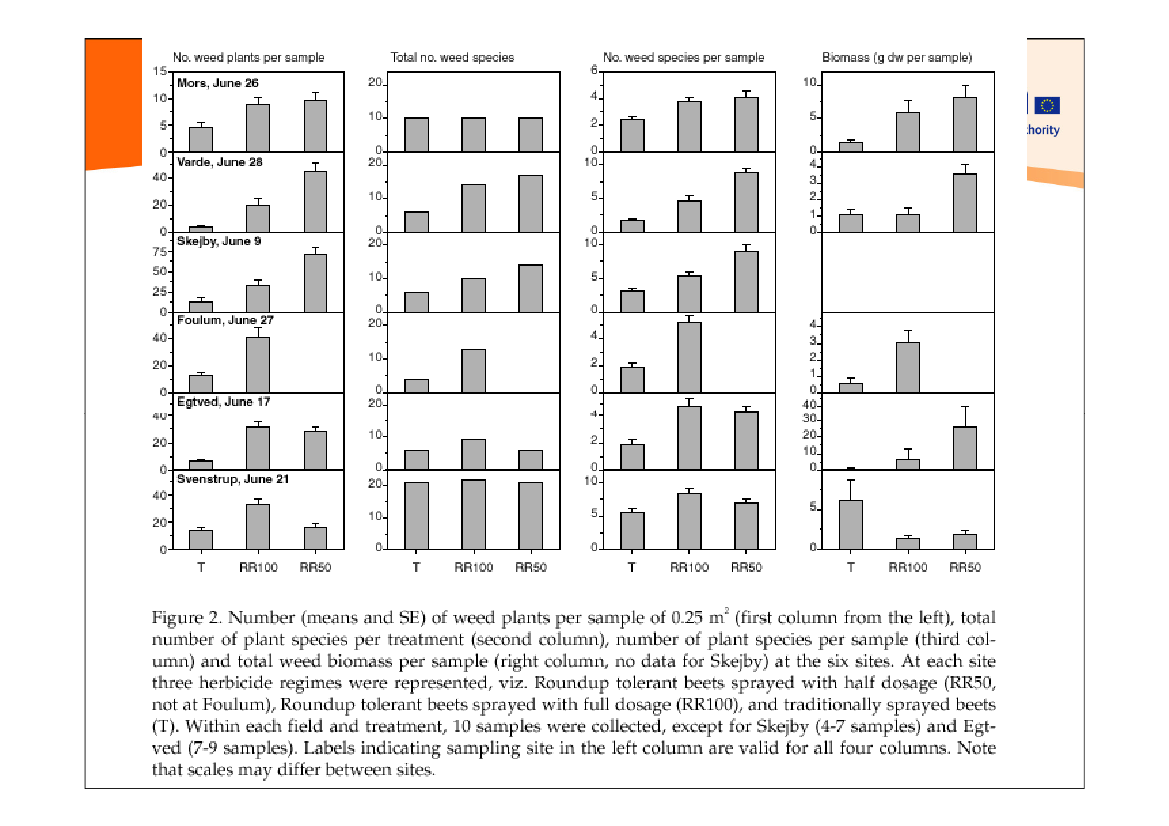
Elmegaard N. &Bruus Pedersen M.NERI (2001)
10
traditional
full
half dosage
11
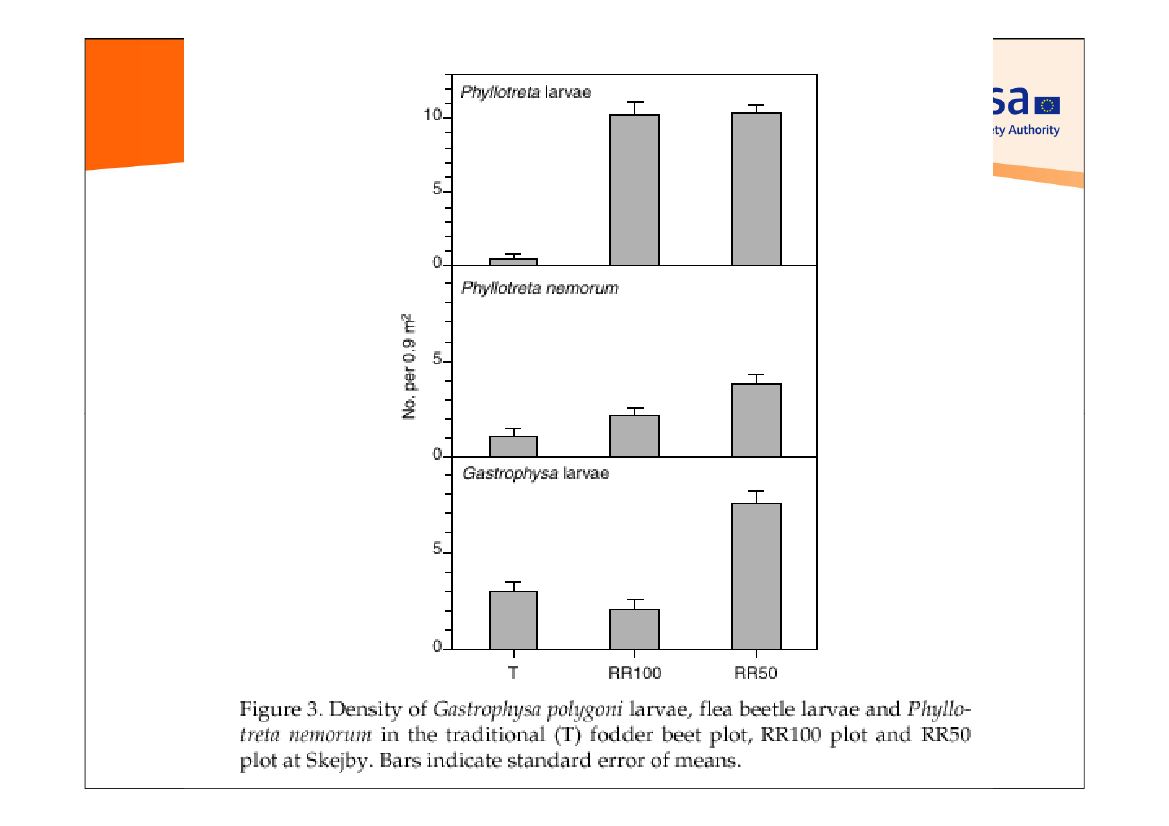
traditional
Roundup 100%
RR 50%
12
Resistant Weeds• Extensive and /or repeated use of same H– Development of resistant weeds– Shifts in weed populations to those that avoidthe Herbicide.Management consequences:- Increased use of Herbicide- Use of Herbicide mixturesEnvironmental Effects:- Reduction in weed diversity (biomass x Spp.)- Reduction in Biodiversity
13
Introduction of GMHT crops intoEuropean agriculture•Should learn from mistakes in N and S America and 50years of Herbicide use worldwide•Not feature extensive overuse of 1 HT system•Should be introduced sustainably into EU agric systemsconsidering:–Crop ecosystems–IPM–Weed resistance management–Volunteer control•AgChem and BioTech Co’s should develop and promoteclear strategy and framework for EU farming regions andsystems.•Stewardship of GMHT crop and Herbicide fits within thisframework14
EFSA Opinion NK603 maizeGMO Panel concluded :•Herbicide Management could result in loss ofbiodiversity and cause environmental harm.GMO Panel recommended:•Herbicides are managed so as to maintain orimprove current levels of biodiversity in cropsand fields.•Risk managers ( eg CAs and EC ), together withApplicants, put in place appropriate managementsystems for use of the herbicides on GMHTcrops.•This should be done under existing pesticide15regulations and regimes operating in MS…..
EFSA Guidance on HT crops (GM)Proposed procedure :1. The potential environmental impacts of therecommended herbicide management systemsshould be compared with those currentlyobserved in equivalent non-HT crops and non-GMHT crops.
16
ERA Guidance Proposals
2.
ERA should consider whether the use of theherbicide could result in reductions inbiodiversity leading to environmentaldamage greater than non-HT crops andnon-GMHT crops.
17
ERA Guidance Proposals3. The applicant should consult the appropriate CA’s
dealing with environmental protection, farmland
biodiversity and pesticide registration in each MS on:
GMHT herbicide programmes that optimize weed
management while maintaining adverse
environmental impacts at or below current levels, and
which are in line with environmental protection goals
and biodiversity action plans of each MS. The
applicant should consider developing herbicide
management strategies to prevent potential adverse
effects to both crop and adjacent non-crop
environments.
(eg unsprayed headlands)18