Udenrigsudvalget 2009-10
URU Alm.del Bilag 139
Offentligt
IDA – A Fund for the Poorest CountriesNordic Baltic Parliamentary Meeting on the World BankFolketinget – CopenhagenJanuary 25, 2010
Roadmap
•IDA’s work in low-income countries•The IDA16 replenishment•Voice and Participation in the World Bank Group
2
Members of the World Bank GroupInternational Bank for Reconstruction and Development - IBRDEstablished 1944 | 186 MembersFiscal 2009 lending: $32.9 billion for 126 new operations in 42 countries•Supports Middle-income Countries through loans, guarantees and advisory work•Funds itself through issuance of AAA bonds in the international capital markets
International Development Association - IDAEstablished 1960 | 169 MembersFiscal 2009 commitments: $14.0 billion for 177 new operations in 63 countries•Supports the world’s poorest countries through soft-loans, grants and guarantees•Is replenished through periodic donor contributions, World Bank Group net income and credit reflows
International Finance Corporation - IFCEstablished 1956 | 182 MembersFiscal 2009: $10.5 billion committed for 447 projects in 103 countries•Supports the private sector through loans, equity and guarantees; funds itself through AAA bonds
Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency - MIGAEstablished 1988 | 174 MembersSupports investors in developing countries through political risk insurance
International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes - ICSIDEstablished 1966 | 143 Members• Provides mediation and arbitration services for investors in developing countries3
IDA – A fund for the poorest countries•Created in 1960, IDA is arevolving solidarity fund.•IDAprovides interest-free loans and grantsfor programs that fostereconomic growth and help reduce poverty and inequalities in poorcountries.More than half of IDA’s assistance goes toSub-Saharan Africa.IDAconcessional creditshave no interest charge, and credit repayments arestretched over 40 years, including a 10-year grace period.IDA provides about 20% of its financing throughoutright grantsto poorcountries at risk of debt distress.
•IDA also provides interest rate and currency risk management;technical assistance and policy advice; and global knowledgeservices including through economic sector work and countrystudies.4
IDA has grown substantially over time
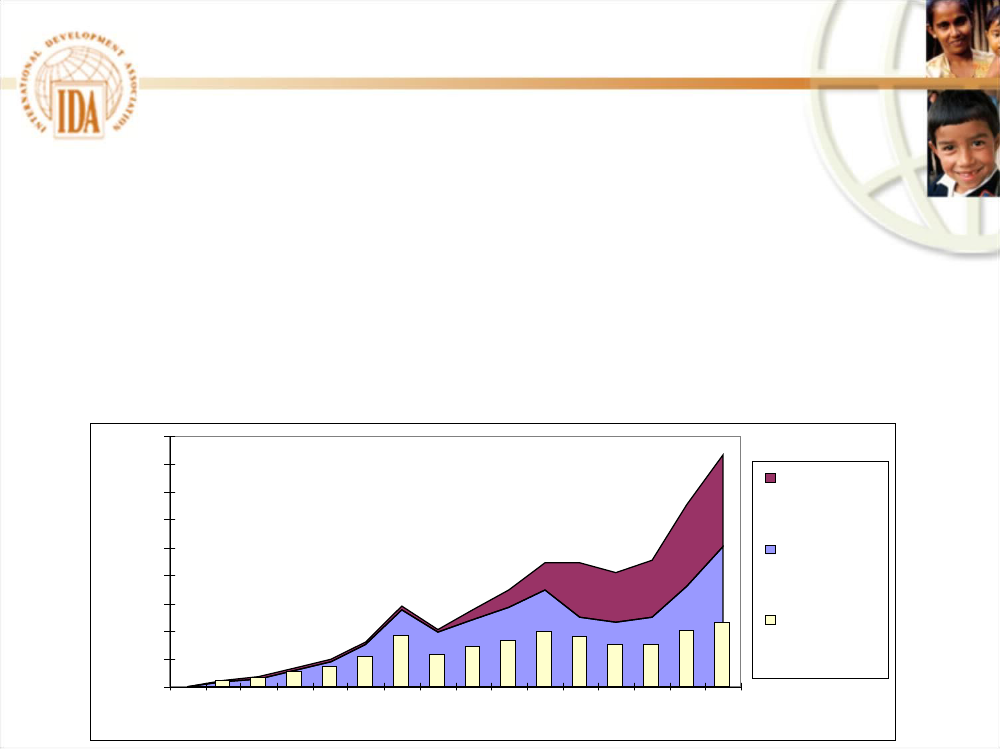
Since 1960, IDA credits and grants exceeded $200 billion.IDA grew by 10% per year. After inflation, however, IDA has been nearly flatover the past three decades.IDA14 (2006-2008) provided $32 billion over 3 years, some $11 billion per year.IDA15 (2009-2011) will provide $42 billion, or some $14 billion per year.
Credit reflows are an increasingly important part of IDA’s financial backing.Debt relief and IDA grants have, however, cut IDA’s reflows.45,00040,00035,00030,00025,00020,00015,00010,0005,0000Ini tialIDA1IDA2IDA3IDA4IDA5IDA6IDA7IDA8IDA9IDA10IDA11IDA12IDA13IDA14IDA15
Total size of IDA Replenishments($ million)
Internal andotherres ourcesDonorcontributionsTotalres ources inreal term s
5
IDA Members•IDA has 169 member countriestoday, including:79 recipient countries- the world’s poorest countries(GNI per capita of less than $3 per day).These countries are home to 2.5 billion people, or half the total populationof the developing world.An estimated 1.5 billion people there survive on less than $2 per day.
35 countries that have graduated from IDA(of which 8 countrieshave ‘reverse-graduated’)45 donor countries,including former IDA recipients (China,Egypt, Korea, Turkey) plus Middle-income Countries andemerging new donors (such as Brazil, Mexico, Russia, SouthAfrica, countries in Eastern Europe).6
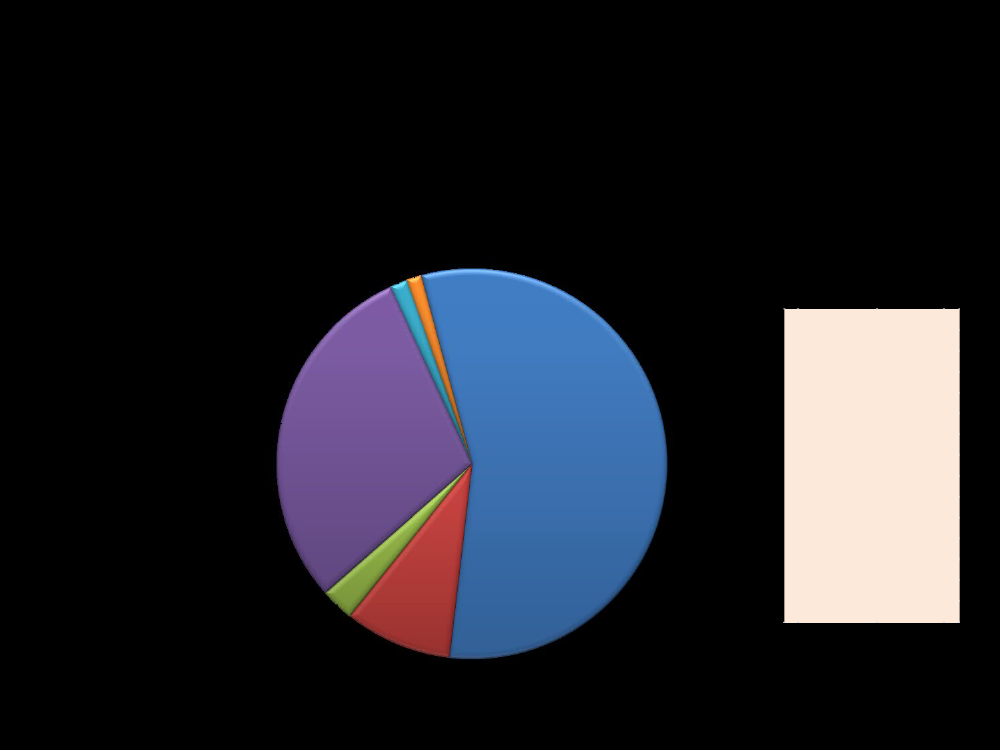
In 2009, IDA allocated 56% to AfricaShare of IDA Financing in Fiscal Year 2009 of $14 billion
Top-10 IDA Borrowersin FY 2009 ($ billion)NigeriaPakistanEthiopiaVietnamBangladeshIndiaTanzaniaGhanaCongo, DRKenya$1,760$1,610$1,175$1,149$1,097$956$783$550$535$525
7
IDA allocates resources to countriesbased on performance and needs
IDA’s resource allocation system- adopted by other IFIs and donors:
Annual allocations, balancing country performance(ratings) andcountry needs(population size and per capita income)Terms of assistance(grants vs. soft loans)determined by debtsustainability
Research shows thatbetter policies lead to better development outcomes
Performance is assessed annually through a rigorous Country Policy andInstitutional Assessment (CPIA), with heavy emphasis on good governancePerformance ratings are publicly disclosed
Allocation system provides exceptions:
Higher assistance to post-conflict countriesfor a period of 10 years (including6 years of gradual phase down to normal levels)Regional integration emphasizedwith a special allocation for regional projectsto supplement national country allocations8
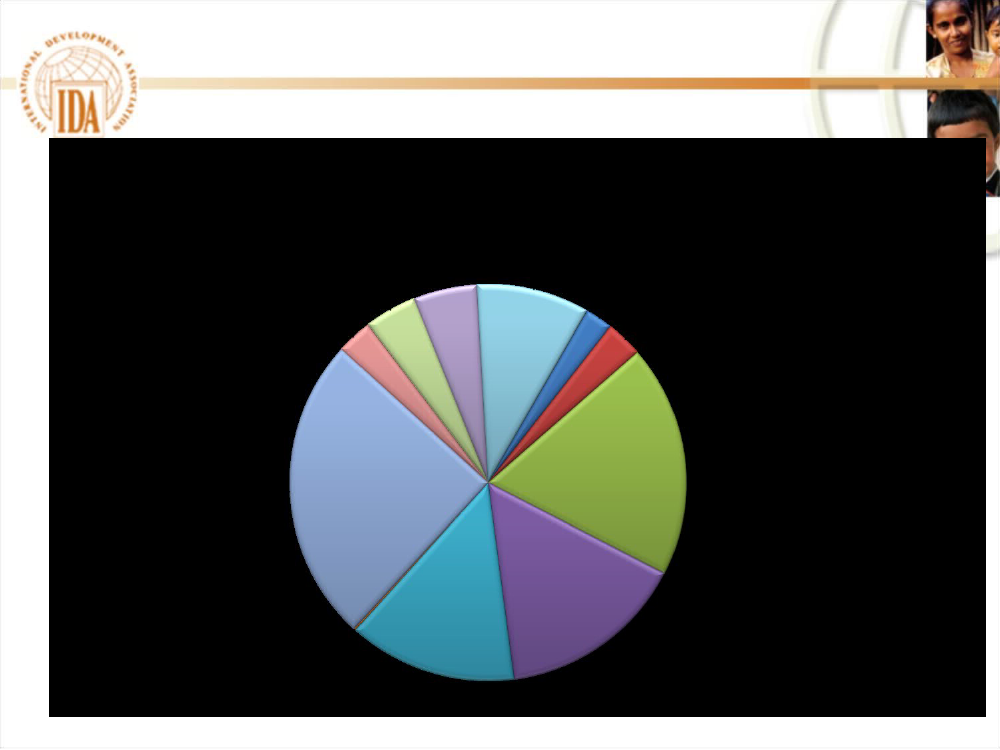
In Africa: Focus on Rural and Human Developmentand the Financial & Private SectorsWorld Bank Assistance to Africa, by Theme, Fiscal Year 2009
9
IDA is country-based and results-driven
10
Examples of IDA’s Results (FY 2006-09)
Education andHealth
1 million additional teachers became qualified to teach at primary level600,000 additional classrooms were constructed or rehabilitatedMore than 7 million people gained access to basic health, nutrition or population services275,000 health personnel trained, and 2,000 health facilities constructed, renovated or equipped7.2 million children received a does of Vitamin A, and over 800,000 children have been immunized7.8 million pregnant women received ante-natal care18.5 million insecticide-treated malaria nets were purchased and/or distributed2,480 km of rural roads constructed or rehabilitated1,790 km of non-rural roads constructed or rehabilitatedAbout 8,500 community water points were constructed or rehabilitatedAbout 60,500 new piped household water connections were establishedAnother 146,500 water connections were rehabilitated1,360 water utilities and water service providers are being supported11
Road Transportand Water Supply
More IDA results at www.worldbank.org/ida
12
Another form of results: IDA Graduates
Country
Year ofLast IDA Credit
Year of Reverse-Graduation to IDA
Country
Year ofLast IDA Credit
Year of Reverse-Graduation to IDA
ChileColombiaCosta RicaNigeriaCote d'IvoireDominican Rep.KoreaTurkeyBotswanaEcuadorSyriaMauritiusMoroccoSwazilandEl SalvadorParaguayTunisiaJordan
196119621962196519731973197319731974197419741975197519751977197719771978
19891992
ThailandHondurasCameroonNicaraguaCongoPapua New GuineaZimbabweEq. GuineaPhilippinesSt. KittsChinaEgyptFYR MacedoniaSerbiaAlbaniaIndonesiaMontenegro
19791980198119811982198319831993199319941999199920022007200820082008
199119941991199420031992
13
Roadmap
•IDA’s work in low-income countries•The IDA16 replenishment•Voice and Participation in the World Bank Group
14
Outcome of the IDA15 Replenishmentin USD equiv. billion
SourcesNew Donor PledgesReflowsof which: Debt relief under MDRI
IDA1312.59.20.0
IDA1417.712.73.8
IDA15As Agreed25.212.66.3
IDA15 vs. IDA14USD bnin %
7.5-0.12.5
42%-1%66%
Agreed IBRD/IFC TransfersTotal FundingAdditional IBRD/IFC TransfersTotal actual funding
0.922.6
1.632.10.4
3.941.7
2.39.7
140%30%
Size of IDA Replenishments,32.5IDA1 – IDA15, $ million1.2721.4641.524
FX rate used: USD/SDRNote: Numbers may not add up due to rounding
IDA15 provides some $42 billion, or $14 billion per year.This compares withsome $11 billion per year in IDA14, and some $8 billion in IDA13.45 donors support IDA15,including 6 new donors to IDA (China, Cyprus,Egypt, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania)European donors provide some 62%of total donor funding in IDA15Strongcontribution from World Bank Group net income(IBRD and IFC)15
Roadmap for the IDA16 discussions•November 18-20, 2009:IDA15 Mid-term Review–Review of IDA15 implementation progress–Consideration of a Crisis Response Window
•Spring 2010:First IDA16 meeting–Agreement on area of thematic focus for IDA16 discussions
•Summer 2010:Second IDA16 meeting–Main forum for development policy discussions–Focus on the financing needs of Low-income countries
•Fall 2010:Third IDA16 meeting–Concluding the policy discussions, reviewing financing parameters
•End of 2010:Final IDA16 meeting–Final donor pledging and burden-sharing16
Roadmap
•IDA’s work in low-income countries•The IDA16 replenishment•Voice and Participation in the World Bank Group
17
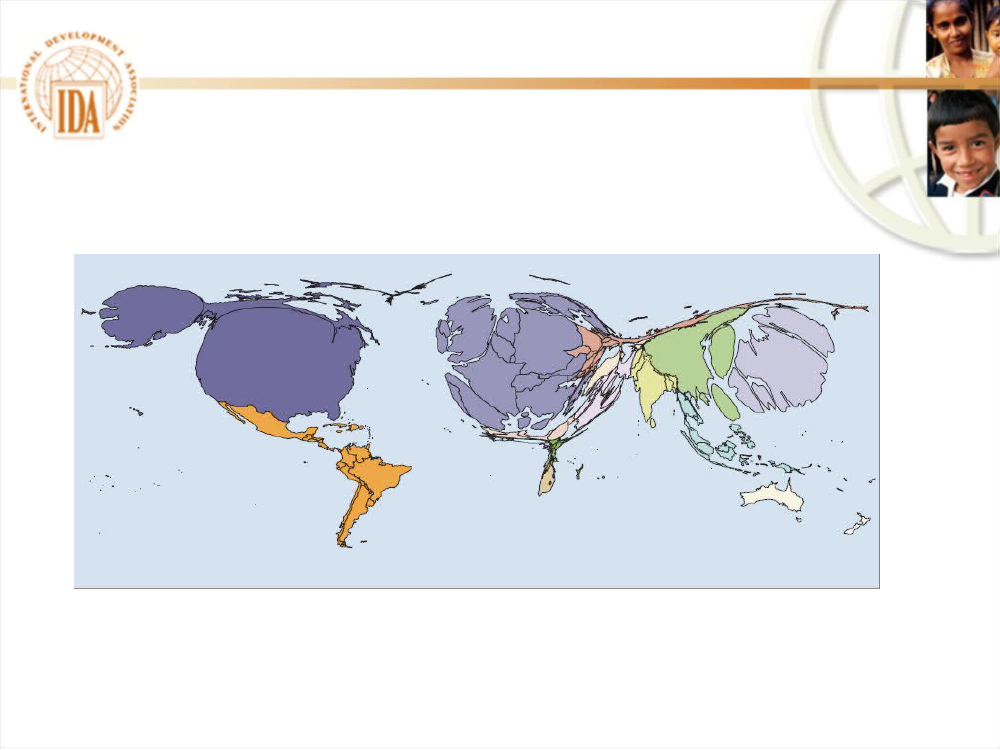
The weight of economies will continue to shift
The World according toend-of-20thcentury economics
Graphic fromWorld Development Report, 2009
18
Voice Reforms - Phase 1 (October 2008)•IBRD Voting Power and Shareholding–Doubled IBRD Basic Votes–Initial realignment of IBRD shareholding , through unallocated sharesRaises Developing and Transition Countries (DTCs) voting power in IBRD by 1.5%,from 42.6% to 44.1%
•
IDA Voting Power–Established Voice Trust Fund for subscriptions by poorest IDA members;Norway, France, Spain and Switzerland have contributed to the Trust Fund–Encouraged other IDA members to take up their available IDA subscriptionsGoal: Raise DTC (Part II) voting power from 43.6% at present to 48.3% (max. potential)
•
Effective Representation at the Board–Added 3rdBoard Chair for Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA has a total of 47 member countries)–Measures to strengthen Board efficiency and cost effectiveness
•
Responsiveness to DTC Views on Development–Stronger DTC representation among Bank management and staff; further decentralizationof World Bank operations–Process for selection of World Bank President that is merit-based, transparent and open19
Voice Reforms - Phase 2 (Spring 2010)Istanbul 2009—Development Committee Communiqué
“ We committed to pursue governance and operational effectivenessreform in conjunction with voting reform to ensure that the World Bank isrelevant, effective, and legitimate. We stressed the importance ofmovingtowards equitable voting powerin the World Bank over time through theadoption of a dynamic formula which primarilyreflects countries’ evolvingeconomic weight and the World Bank’s development mission,and thatgenerates in the next shareholding review a significantincrease of at least3% of voting power for developing and transition countries,in addition tothe 1.46% increase under the first phase of this important adjustment, tothe benefit of under-represented countries. While recognizing that over-represented countries will make a contribution, it will be important toprotect the voting power of the smallest poor countries.We recommittedto reaching agreement by the 2010 Spring Meetings.”20
Voice Reforms - Phase 2 (Spring 2010)•IBRD Shareholding Review–––––Further shift for DTCs by at least 3%, to a total of 47%To be achieved through a Selective Capital IncreasePrimary criteria is economic weight in the world economyContributions to Bank’s development mandate (IDA) also under considerationFuture IBRD shareholding reviews at regular intervals
•
IFC Voice Reform–Current DTC shareholding at IFC: 33.4%–Spring 2010 is also target for IFC Voice reform–Discussions of contours of IFC Voice reform are ongoing
•
Institutional Reforms––––Management is further increasing staff diversity and decentralization of Bank operationsOngoing internal governance improvementsReport of High Level Commission on Modernization of WBG Governance (Zedillo)Spring 2010 Development Committee will review progress
21
22